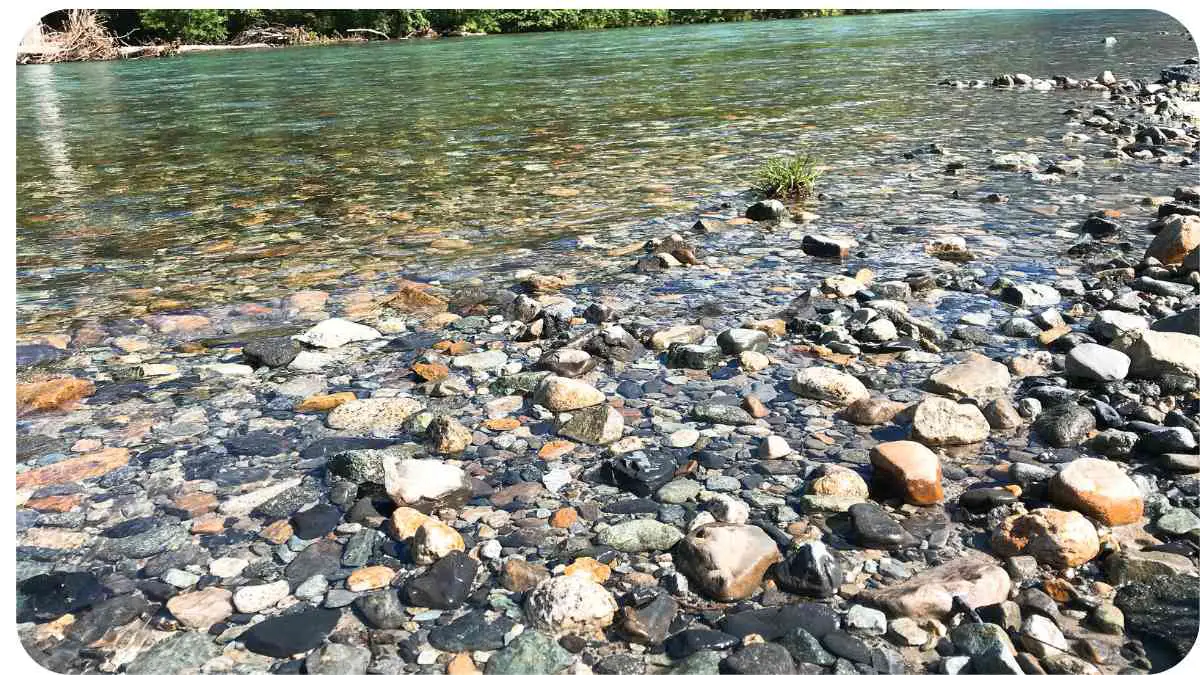
Riverbank erosion is a natural process where the river’s flow wears away the land along its banks. While some degree of erosion is normal, unchecked erosion can lead to significant land loss and environmental damage. This process can be accelerated by various factors, including human activities and extreme weather conditions.
| Key Takeaways |
|---|
| Understand Riverbank Erosion: Recognize the causes and impacts of riverbank erosion to address it effectively. |
| Use Vegetative Solutions: Implement native plants and ground covers to stabilize and protect riverbanks. |
| Apply Structural Solutions: Consider riprap, gabions, bulkheads, and retaining walls for robust erosion control. |
| Explore Hybrid Approaches: Combine vegetative and structural methods for enhanced stability and effectiveness. |
| Monitor and Maintain: Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial for long-term success of erosion control measures. |
| Learn from Case Studies: Study real-world examples to understand successful strategies and apply best practices. |
| Utilize Resources: Refer to guides, blogs, and resources for additional insights and techniques in erosion control. |
Importance of Combating Riverbank Erosion
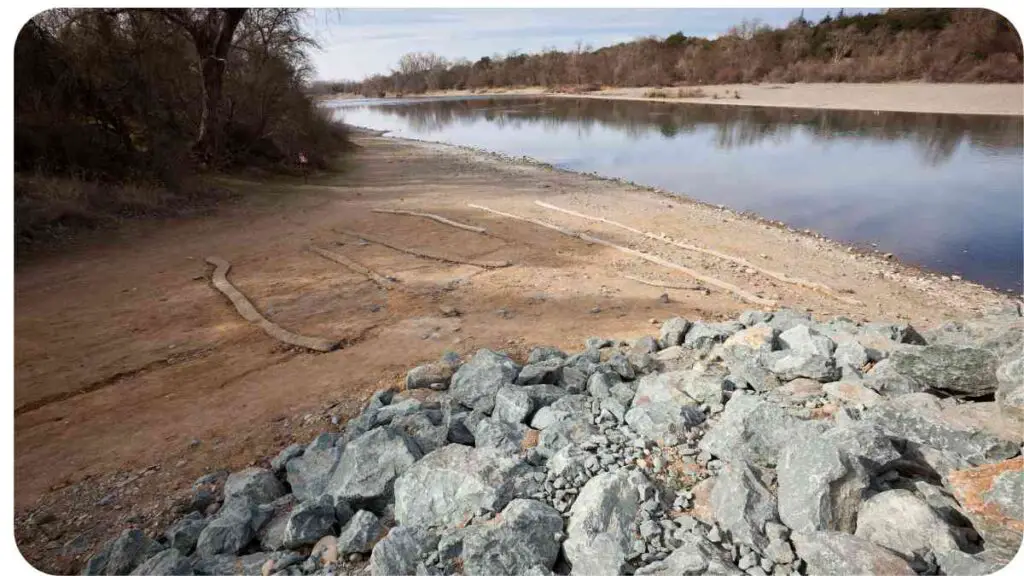

Addressing riverbank erosion is crucial for protecting property, maintaining natural habitats, and ensuring the stability of river ecosystems. Effective erosion control helps preserve the land and prevent the loss of valuable soil, which is essential for plant growth and supporting wildlife.
Understanding how to address soil erosion is crucial for maintaining a stable landscape. For effective solutions, check out this guide on addressing soil erosion in sloped landscapes. Implementing these strategies can help prevent further damage.”
Understanding Riverbank Erosion
Causes of Riverbank Erosion
Riverbank erosion can result from a combination of natural and human-induced factors. Common causes include:
- Water Flow: Fast-moving water can erode the bank material.
- Weather Events: Heavy rainfall and floods can increase the rate of erosion.
- Human Activities: Construction, deforestation, and improper land use can exacerbate erosion.
Effects on the Environment
Erosion can lead to several environmental issues, including:
- Loss of Habitat: Eroded banks can destroy habitats for plants and animals.
- Water Quality: Sediment from erosion can reduce water quality and affect aquatic life.
- Soil Degradation: Erosion leads to the loss of fertile soil, impacting agriculture and natural vegetation.
Key Indicators of Erosion
Identifying erosion early is crucial for effective intervention. Look for:
- Bare Soil: Areas where vegetation has been stripped away.
- Eroded Channels: Visible signs of soil being washed away.
- Sediment Accumulation: Increased sediment in the river or surrounding areas.
If you’re dealing with waterlogged garden beds, it’s essential to find a solution quickly. Our article on soil not draining solutions for soggy garden beds offers practical tips to improve drainage and plant health.
Preventive Measures
Vegetative Solutions
Native Plants and Grasses
Using native plants and grasses is an effective way to stabilize riverbanks. These plants have deep root systems that help hold the soil in place. Examples include:
| Plant Type | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Grasses | Erosion control, fast-growing | Switchgrass, Big Bluestem |
| Shrubs | Soil stabilization, wildlife habitat | Red Osier Dogwood, Arrowwood Viburnum |
| Trees | Long-term stabilization, shade | Willows, River Birch |
Ground Cover Plants
Ground cover plants provide additional protection by reducing the impact of rain and wind on the soil. They also prevent weed growth and improve soil structure.
Structural Solutions
Riprap and Gabions
Riprap consists of large stones placed along the riverbank to absorb and deflect the energy of flowing water. Gabions are wire baskets filled with rocks, used to stabilize eroded banks.
| Solution | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Riprap | Durable, effective against high flow | Can be expensive, requires proper installation |
| Gabions | Flexible design, good for areas with irregular shapes | Less aesthetically pleasing, potential for rusting |
Bulkheads and Retaining Walls
Bulkheads are vertical barriers placed along the riverbank to prevent erosion. Retaining walls can also be used to hold back soil and protect the bank from erosion.
Hybrid Approaches
Combining Vegetative and Structural Methods
Hybrid approaches use both vegetative and structural solutions to create a more robust erosion control strategy. For example, combining riprap with native plants can enhance bank stability and aesthetics.
Landscape renovation can be a significant undertaking. To get a comprehensive view of the process, refer to our ultimate guide to landscape renovation, which provides essential insights and steps for a successful project.
Implementing Vegetative Solutions
Choosing the Right Plants
Selecting appropriate plants is critical for effective erosion control. Consider factors such as soil type, water availability, and local climate when choosing plants for your riverbank.
Planting Techniques
Proper planting techniques include preparing the soil, spacing plants correctly, and ensuring adequate water supply. Using mulch can also help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the long-term success of vegetative solutions. This includes monitoring plant health, replanting as needed, and managing invasive species.
Applying Structural Solutions
Designing Riprap and Gabions
When designing riprap and gabions, consider factors such as the size of stones, basket strength, and proper placement. Ensure that these structures are designed to withstand local water flow conditions.
Retaining walls play a vital role in controlling erosion and managing landscape stability. Learn about common issues and their fixes in our detailed article on retaining wall failures, ensuring your project’s success.
Installing Bulkheads
Proper installation of bulkheads involves anchoring them securely into the soil and ensuring they are level and aligned. This helps prevent future erosion and structural failure.
Building Effective Retaining Walls
Effective retaining walls should be designed to handle soil pressure and water flow. Use appropriate materials and construction techniques to ensure durability and stability.
Hybrid Approaches in Detail
Benefits of Combining Methods
Hybrid approaches offer the advantages of both vegetative and structural solutions. They provide comprehensive protection, enhance the aesthetic appeal of the riverbank, and improve overall stability.
Case Studies and Examples
Explore real-world examples of successful hybrid approaches to riverbank erosion. Learn from the experiences of other projects to apply best practices to your own erosion control efforts.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Example 1: Successful Vegetative Solution
A project in [Location] successfully used native grasses and shrubs to stabilize a riverbank. This approach not only prevented erosion but also restored natural habitat and improved water quality.
Hardscape features like patios can face problems over time. For solutions to common issues, refer to our guide on hardscape heaving and paver problems. This resource helps maintain your outdoor spaces effectively.
Example 2: Effective Structural Solution
In [Location], riprap and gabions were used to address severe erosion issues. The project effectively reduced soil loss and protected property from further damage.
Example 3: Successful Hybrid Approach
A combined approach in [Location] utilized both vegetative and structural methods. This project demonstrated the effectiveness of integrating multiple erosion control strategies for long-term success.
Monitoring and Maintenance

Regular Inspections
Regular inspections are essential for identifying erosion issues early and ensuring that control measures are functioning as intended. Look for signs of wear and tear, and address any problems promptly.
Common Issues and Fixes
Common issues include plant die-off, structural damage, and sediment buildup. Address these issues through replanting, repairs, and ongoing maintenance to ensure continued effectiveness.
Long-Term Maintenance Strategies
Long-term maintenance involves periodic reviews, updates to erosion control measures, and continued care of vegetation. This helps ensure the continued success of your erosion control efforts.
Tools and Resources
Recommended Tools for Riverbank Landscaping
- Soil Test Kits: To analyze soil composition and determine suitable plants.
- Planting Tools: Shovels, trowels, and other tools for planting and maintaining vegetation.
- Erosion Control Materials: Mulch, geotextiles, and other materials to support erosion control efforts.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
Effective riverbank erosion control involves understanding the causes of erosion, implementing appropriate measures, and maintaining solutions over time. Combining vegetative and structural methods can offer comprehensive protection and long-term success.
Final Tips and Advice
When tackling riverbank erosion, start with a thorough assessment of the area and select the most suitable erosion control methods. Regular maintenance and monitoring are key to ensuring the effectiveness of your solutions.
Further Reading
Vegetation Systems for Riverbank Erosion Control
This document provides an in-depth look at various vegetation systems used for controlling riverbank erosion. It covers different plant types, their benefits, and best practices for implementation.
Natural Materials for Riverbank Protection
Explore the use of natural materials in riverbank protection. This blog discusses various eco-friendly options for stabilizing riverbanks and their effectiveness compared to traditional methods.
Riverbank Erosion Solutions
This page offers a comprehensive overview of solutions for riverbank erosion, including both vegetative and structural methods. It provides practical advice and examples for effective erosion control.
FAQs
How does riverbank erosion impact the environment?
Riverbank erosion can lead to habitat loss, decreased water quality, and soil degradation. It affects plant and animal life and can reduce the fertility of the soil, impacting agriculture and natural vegetation.
What are the best plants for controlling riverbank erosion?
Native grasses, shrubs, and trees with deep root systems are ideal for controlling riverbank erosion. Examples include switchgrass, red osier dogwood, and willows. These plants help stabilize the soil and provide natural habitat.
What are the differences between riprap and gabions?
Riprap consists of large stones placed along the riverbank to absorb and deflect water flow, while gabions are wire baskets filled with rocks used for stabilization. Riprap is often more visible, while gabions can adapt to irregular bank shapes.
How often should riverbank erosion control measures be inspected?
Erosion control measures should be inspected regularly, at least once a year, and after major weather events. This helps identify and address any issues early, ensuring the effectiveness of the measures.
Can a combination of methods be more effective for erosion control?
Yes, combining vegetative and structural methods can enhance erosion control. Hybrid approaches leverage the strengths of both methods, providing greater stability and resilience against erosion. For instance, combining riprap with native plants can improve both protection and aesthetics.

Hi! My name is Hellen James, and I’m a landscape designer in Los Angeles. I’ve been working with homeowners and businesses to help them improve the look of their properties for over 10 years.